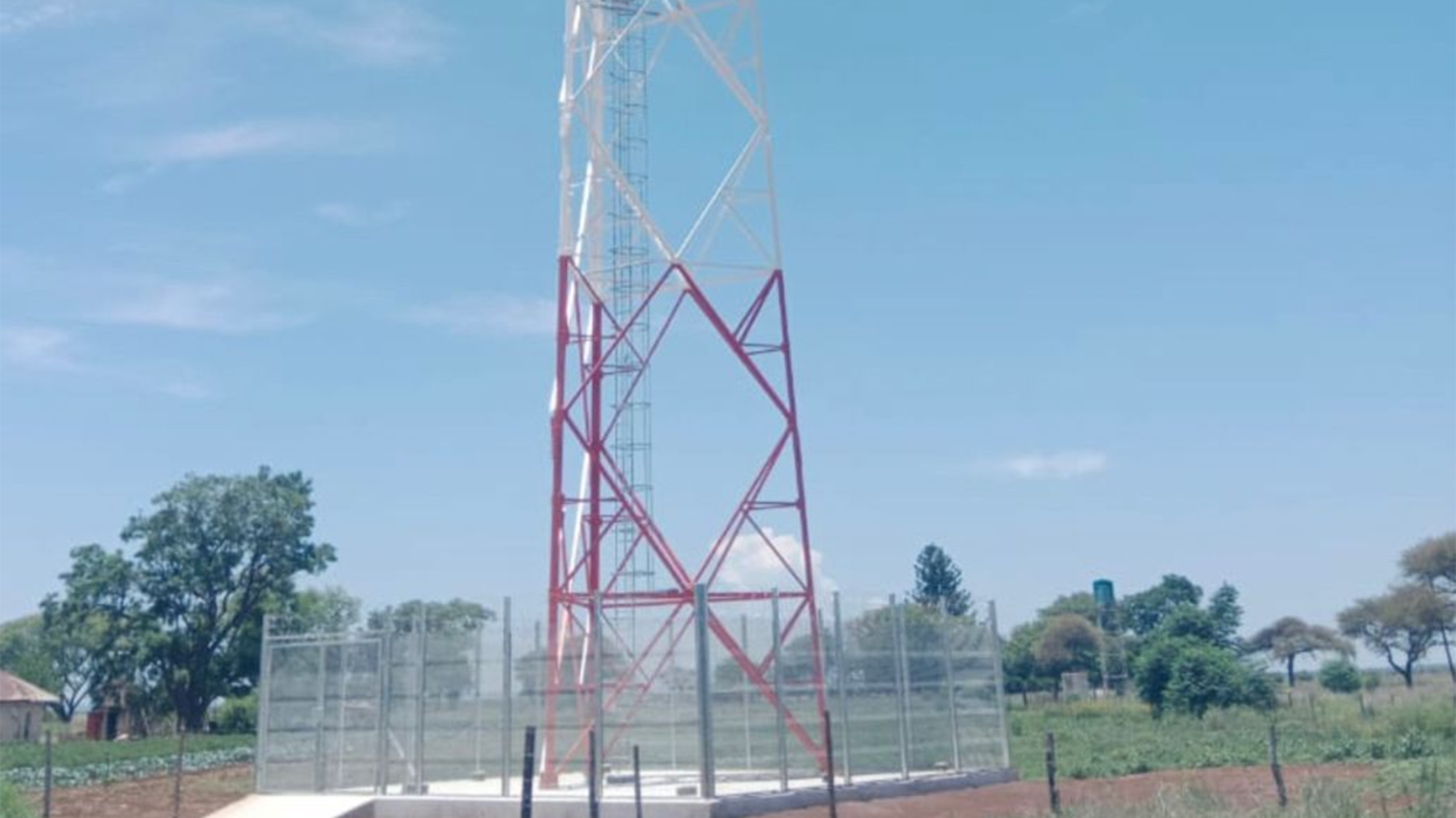
Here are the key differences between 3-legged and 4-legged angular steel towers
Stability - 4-legged towers provide better stability and resistance to lateral loads from wind and uneven terrain. 3-legged towers can require bracing.
Footprint - 4-legged towers have a wider base footprint and spacing between legs for improved support. 3-legged designs occupy less space.
Loading - Weight distribution is more even on 4 legs. 3-legged towers concentrate more load on each leg and foundation.
Height - 4-legged towers can typically reach greater heights while maintaining strength and stability.
Access - Getting access between legs for maintenance can be easier with 3 legs. 4 legs can be more cramped.
Aesthetics - Some may find 3-legged towers more aesthetically pleasing and less visually intrusive.
Cost - 3-legged towers use less material and have simpler foundations, reducing overall cost.
Modularity - 3-legged sections can be more modular for easy transport and assembly. 4-legged sections are heavier.
Redundancy - 4-legged towers offer more redundancy if failure of one leg occurs.
Applications - 4 legs are commonly used for larger transmission towers and in areas prone to high winds. 3 legs for smaller distribution towers.
In summary, 4 legs offer better stability and strength while 3 legs provide more space savings and access. The choice depends on loading, height, cost, and site-specific requirements.

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 ID
ID
 LV
LV
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 UK
UK
 SQ
SQ
 ET
ET
 HU
HU
 FA
FA
 AF
AF
 MS
MS
 GA
GA
 CY
CY
 UR
UR
 EO
EO
 LA
LA
 MN
MN
 TG
TG
 UZ
UZ
 HAW
HAW
 KY
KY
 XH
XH








